ESP32 - Sound Sensor - Servo Motor
In this tutorial, we'll explore how to utilize the sound sensor to control servo motor. Specifically, we'll delve into two exciting applications:
- Sound switch: When sound is detected (e.g knock), the ESP32 rotates servo motor to 90 degree if it's in 0 degree, and 0 degree if it's in 90 degree.
- Sound-activated relay: Upon detecting sound, the ESP32 rotates servo motor to 90 degree for a specific period of time, and then rotates back to 0 degree.
Hardware Used In This Tutorial
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Introduction to Servo Motor and Sound Sensor
If you do not know about servo motor and sound sensor (pinout, how it works, how to program ...), learn about them in the following tutorials:
Wiring Diagram
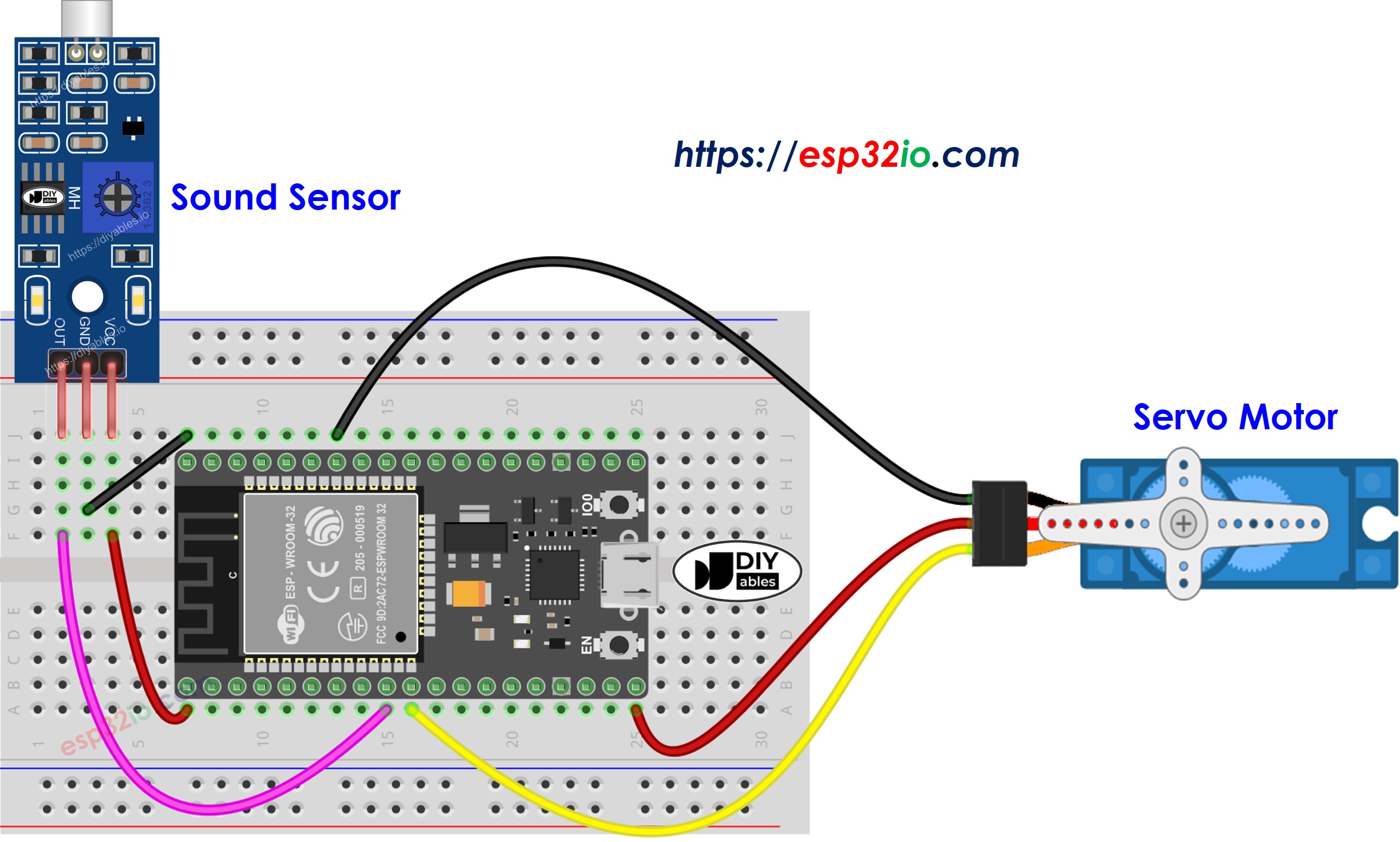
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
If you're unfamiliar with how to supply power to the ESP32 and other components, you can find guidance in the following tutorial: The best way to Power ESP32 and sensors/displays.
ESP32 Code - Sound Switch toggles Angle of Servo Motor
The below code toggles the angle of servo motor between 0 and 90 degree each time the sound is detected.
Quick Instructions
- If this is the first time you use ESP32, see how to setup environment for ESP32 on Arduino IDE.
- Do the wiring as above image.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your PC via a micro USB cable
- Open Arduino IDE on your PC.
- Select the right ESP32 board (e.g. ESP32 Dev Module) and COM port.
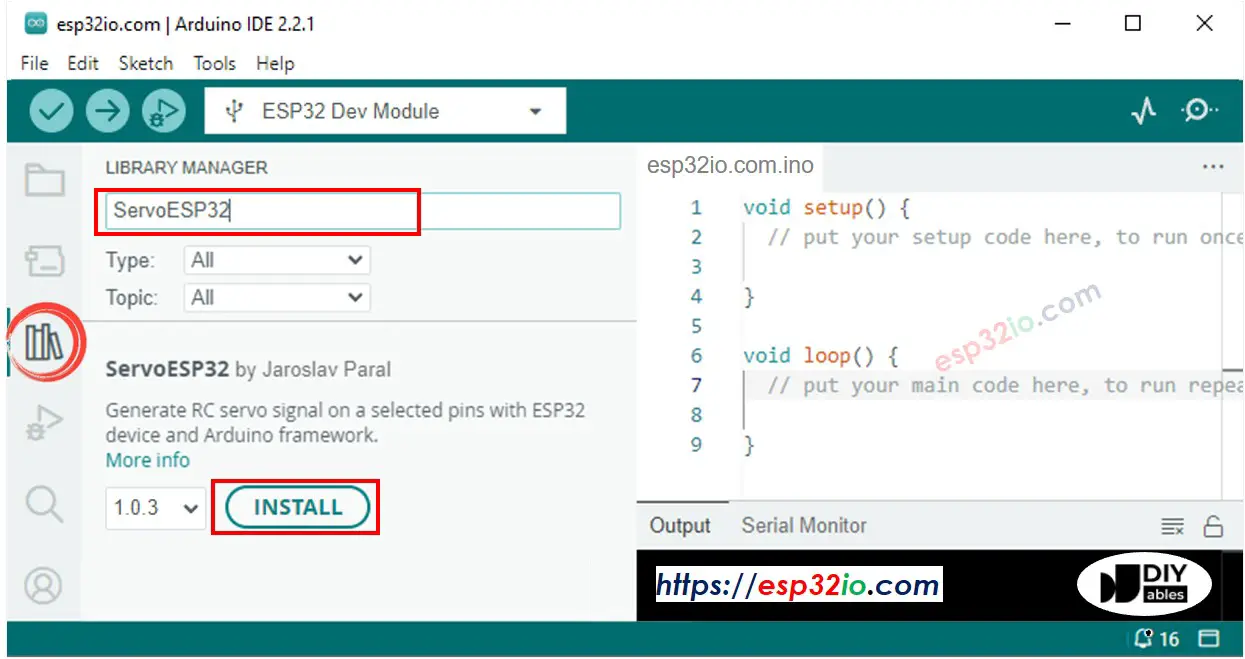
- Click to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Type ESP32Servo on the search box, then look for the servo library by Kevin Harrington,John K. Bennett.
- Click Install button to install servo motor library for ESP32.
- Connect ESP32 to PC via USB cable
- Open Arduino IDE, select the right board and port
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP32
- Clap your hand in front of the sound sensor
- See the change of servo motor
ESP32 Code - Sound-activated Servo Motor for a period of time
The below code rotates the servo motor to 90 degree for a period of time when the sound is detected. After the period of time, the servo motor is rotated back to 0 degree.
Please take note that the code mentioned above utilizes the delay() function for simplicity. However, if you incorporate additional code, it may get blocked during the delay time. To address this, the following code implements a non-blocking approach using the millis() function instead of delay to prevent blocking.
Video Tutorial
Making video is a time-consuming work. If the video tutorial is necessary for your learning, please let us know by subscribing to our YouTube channel , If the demand for video is high, we will make the video tutorial.
