ESP32 - Soil Moisture Sensor
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP32 to read the soil moisture from sensor. In detail, we will learn:
- Capacitive Moisture Sensor vs Resistive Moisture Sensor
- How to use ESP32 to read the value from a capacitive moisture sensor
- How to calibrate a capacitive moisture sensor
- How ESP32 determines if the soil is wet or dry
This tutorial shows how to program the ESP32 using the Arduino language (C/C++) via the Arduino IDE. If you’d like to learn how to program the ESP32 with MicroPython, visit this ESP32 MicroPython - Soil Moisture Sensor tutorial.
Hardware Used In This Tutorial
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Buy Note: Numerous capacitive soil moisture sensors available in the market are of poor quality, regardless of the version. We strongly advise purchasing the sensor with TLC555I Chip from the DIYables brand via the link above; we conducted tests, and it performed reliably.
Introduction to Soil Moisture Sensor Sensor

There are two types of moisture sensors:
- Resistive moisture sensor
- Rapacitive moisture sensor.
Both sensors output the soil moisture value. However, their working principles are different. We highly recommend using the capacitive moisture sensor, because of the following reasons:
- The resistive soil moisture sensor corrodes over time. The electrical current that flows between the sensor's probes causes electrochemical corrosion.
- The capacitive soil moisture sensor does NOT corrode over time. The sensor's electrodes are not exposed and no electrical current folows between them.
The below image shows the corrosion on a resistive soil moisture sensor.
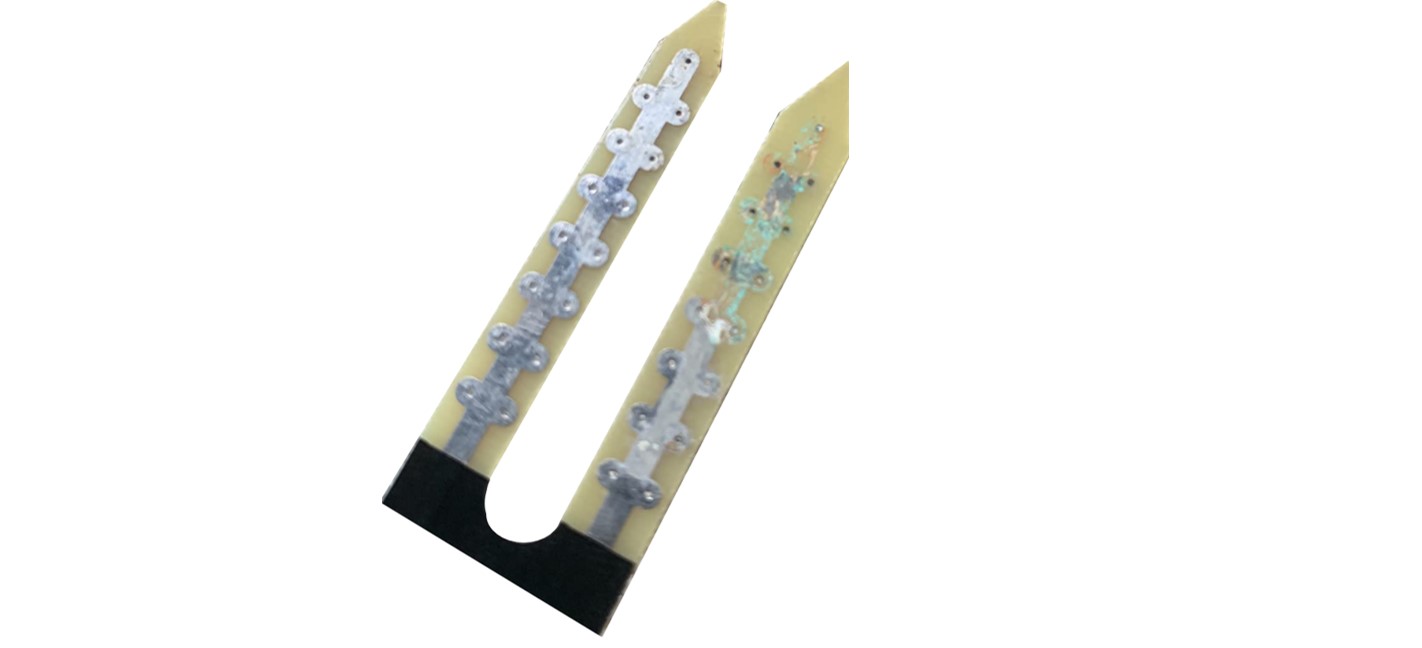

The rest of this tutorial uses the capacitive soil moisture sensor.
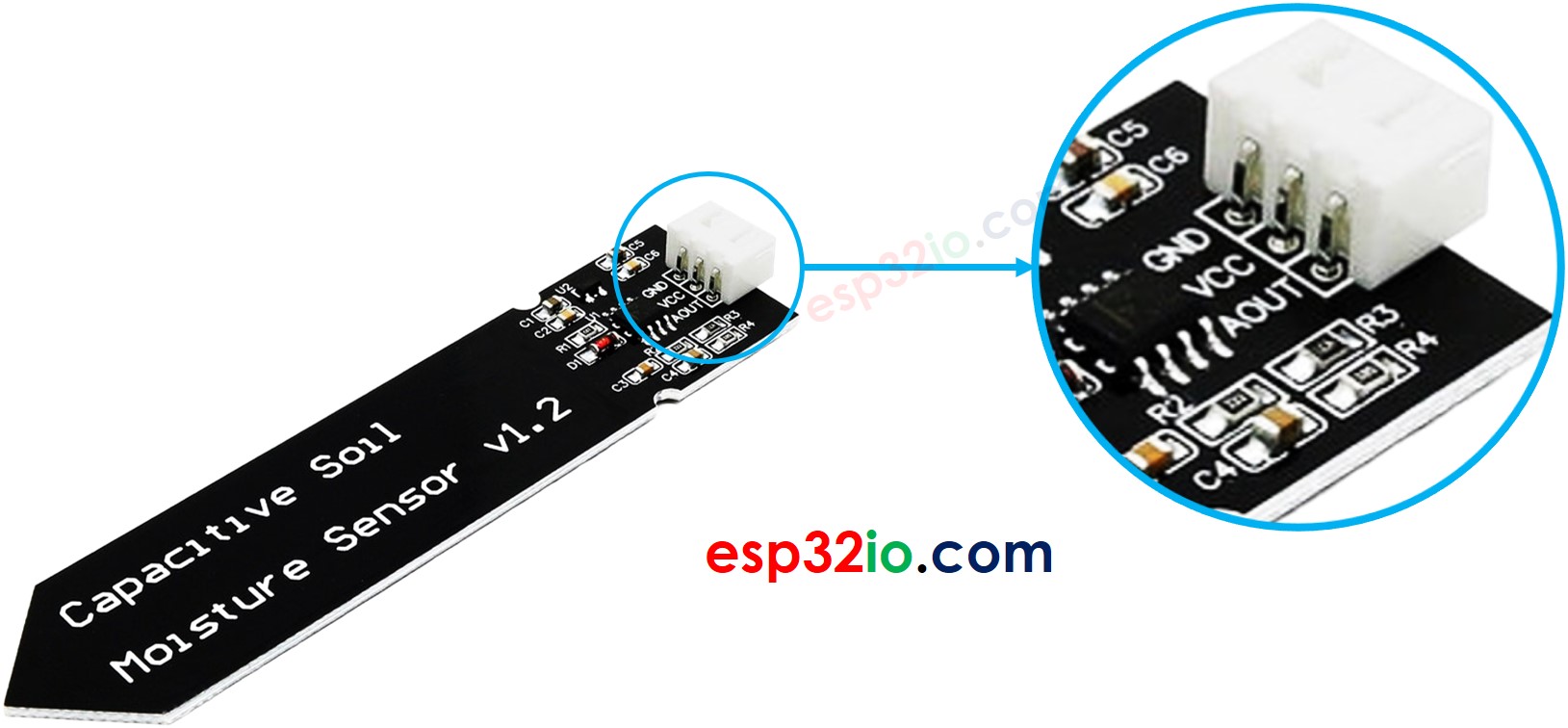
Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Pinout
A capacitive soil moisture sensor has three pins:
- GND pin: connect this pin to GND (0V)
- VCC pin: connect this pin to VCC (5V or 3.3v)
- AOUT pin: Analog signal output pin outputs the voltage in inverse proportion to the soil moisture level. Connect this pin to an ESP32's analog input pin.

How It Works
The more the water presents in the soil, the lower the voltage in the AOUT pin is
Wiring Diagram
- How to connect ESP32 and soil moisture sensor using breadboard
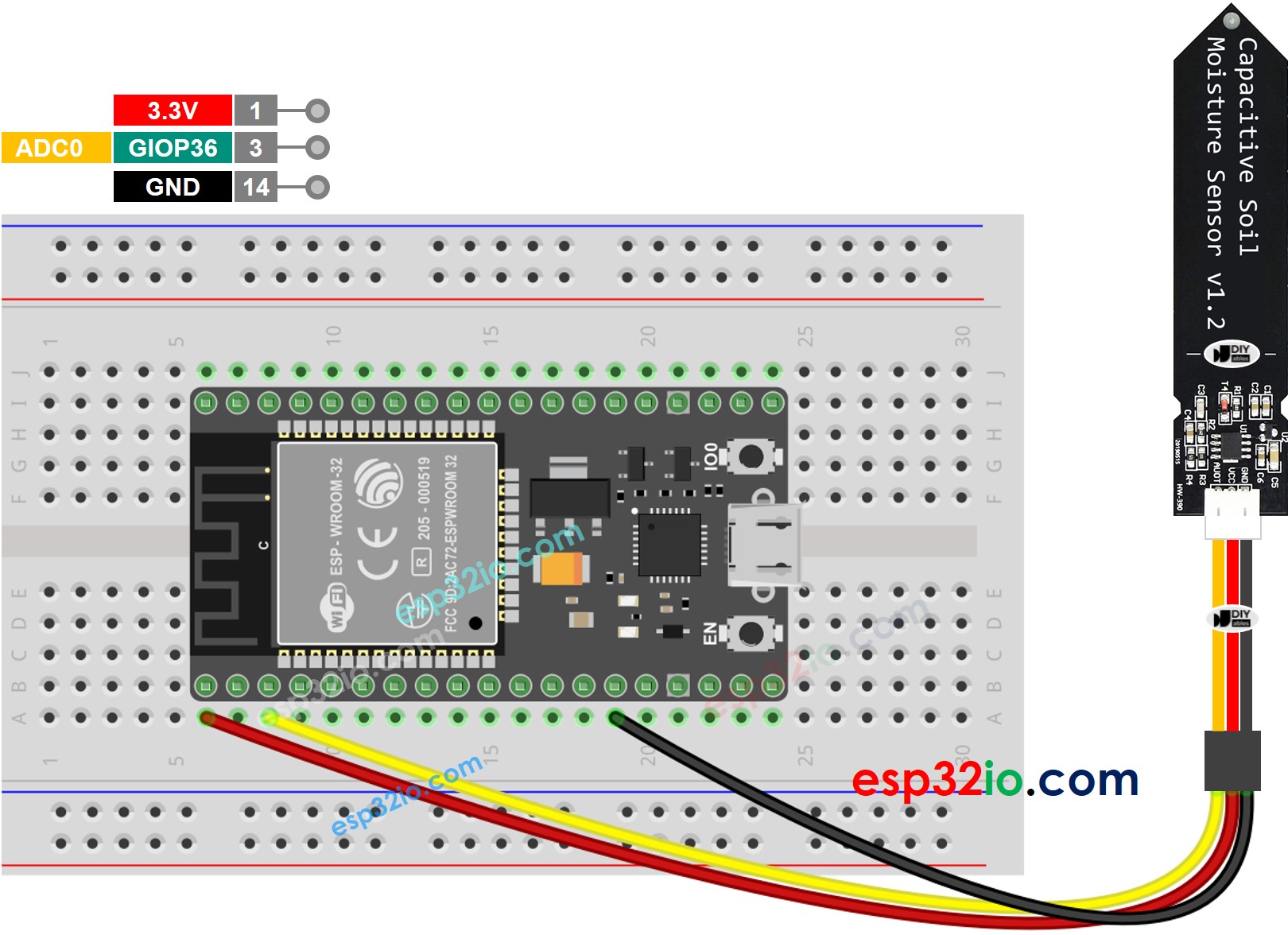
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- How to connect ESP32 and soil moisture sensor using screw terminal block breakout board (powered via USB cable)
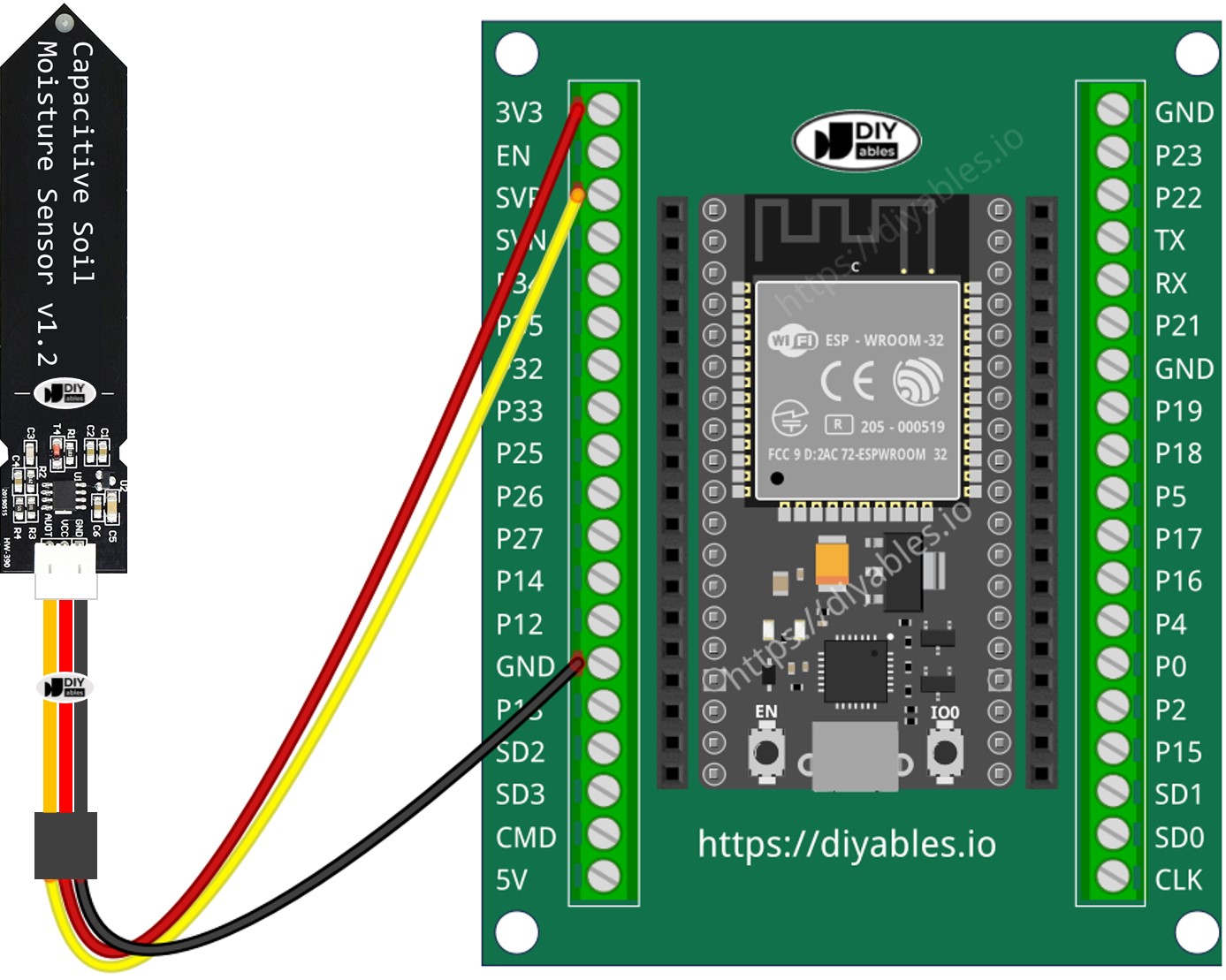
If you're unfamiliar with how to supply power to the ESP32 and other components, you can find guidance in the following tutorial: The best way to Power ESP32 and sensors/displays.
ESP32 Code
Quick Instructions
- Copy the above code and paste it to Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP32 board
- Bury the sensor in soil, then pour water into the soil. Or slowly submerge it into a cup of salt water.
- Check out the result on Serial Monitor. It looks like the below:
※ NOTE THAT:
- Avoid using pure water for testing, as it doesn't conduct electricity, thus won't affect sensor readings.
- The sensor readings never reach zero. It's normal for the values to range between 3100 and 2600, although this may vary depending on some factors: the depth of sensor embedding, the composition of the soil or water, voltage of power supply.
- Do not bury the circuit part (located on top of the sensor) in soil or water, as this could potentially damage the sensor.
Calibration for Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor
The measured value from the moisture sensor is relative. It depends on the soil's composition and water. In practice, we need to do calibration to determine a threshold that is a border between wet and dry.
How to do calibration:
- Run the above code on ESP32
- Plant the moisture sensor into the soil
- Plant the moisture sensor into the soil
- Irrigate the soil slowly
- Watch Serial Monitor.
- Write down a value at the time you feel that the soil changes its moisture from dry to wet. This value is called THRESHOLD.
Determine if the soil is wet or dry
After the calibration, update the THRESHOLD value you wrote down to the below code. The below code determines if the soil is wet or dry
The result on Serial Monitor.
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a soil moisture sensor. The ESP32 ADC is good for projects that do NOT need high accuracy. However, for projects that need precise measurements, please note:
- The ESP32 ADC is not perfectly accurate and might need calibration for correct results. Each ESP32 board can be a bit different, so you need to calibrate the ADC for each individual board.
- Calibration can be difficult, especially for beginners, and might not always give the exact results you want.
For projects that need high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g ADS1115) with the ESP32 or using an Arduino, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still want to calibrate the ESP32 ADC, refer to ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver
Video Tutorial
Making video is a time-consuming work. If the video tutorial is necessary for your learning, please let us know by subscribing to our YouTube channel , If the demand for video is high, we will make the video tutorial.
