ESP32 - GPS
In this guide, we'll discover how to extract GPS coordinates (longitude, latitude, altitude), GPS speed (in kilometers per hour), and date-time information from the NEO-6M GPS module. Additionally, we'll explore the process of calculating the distance between the current GPS position and a predefined set of GPS coordinates (such as the coordinates of London).
Hardware Used In This Tutorial
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
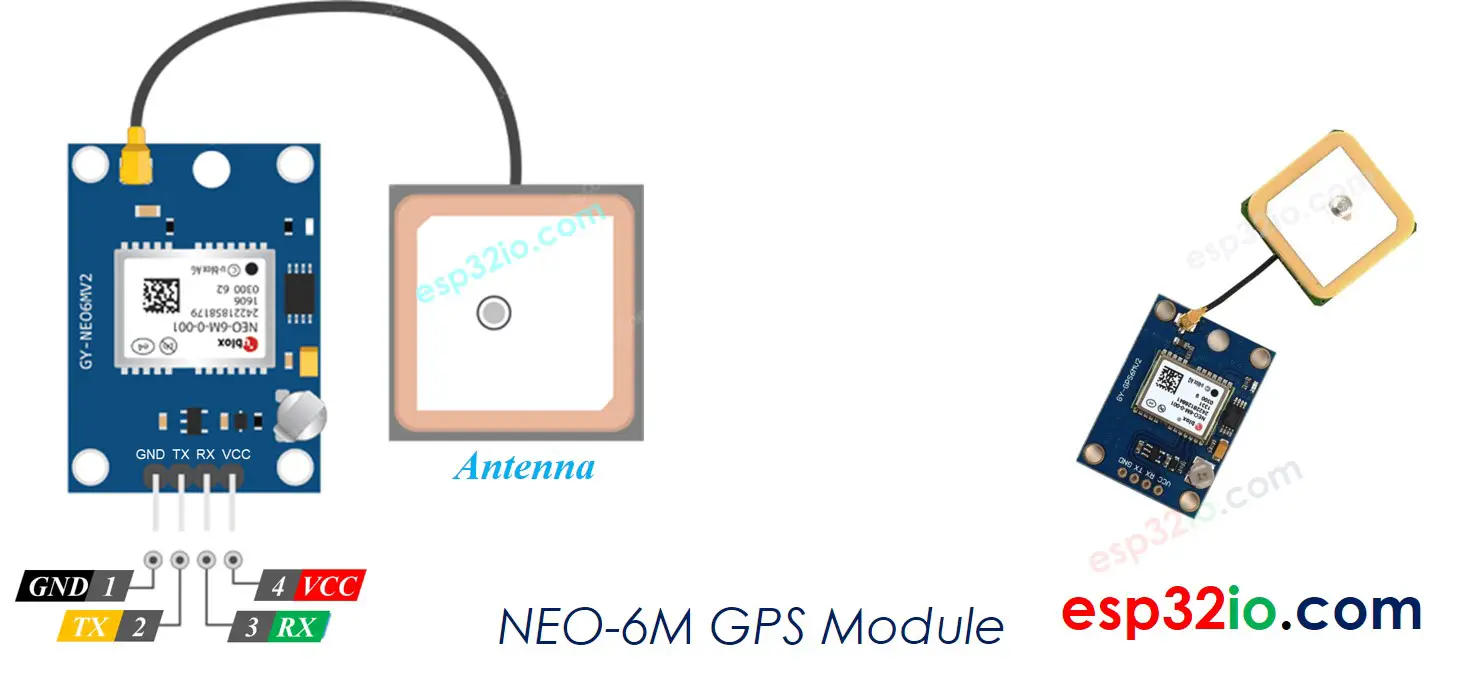
Introduction to NEO-6M GPS module
Pinout
The NEO-6M GPS module has 4 pins:
- VCC pin: needs to be connected to VCC (5V)
- GND pin: needs to be connected to GND (0V)
- TX pin: is used for communication between the GPS module and ESP32, needs to be connect to Serial RX pin on ESP32.
- RX pin: is used for communication between the GPS module and ESP32, needs to be connect to Serial TX pin on ESP32.
Wiring Diagram
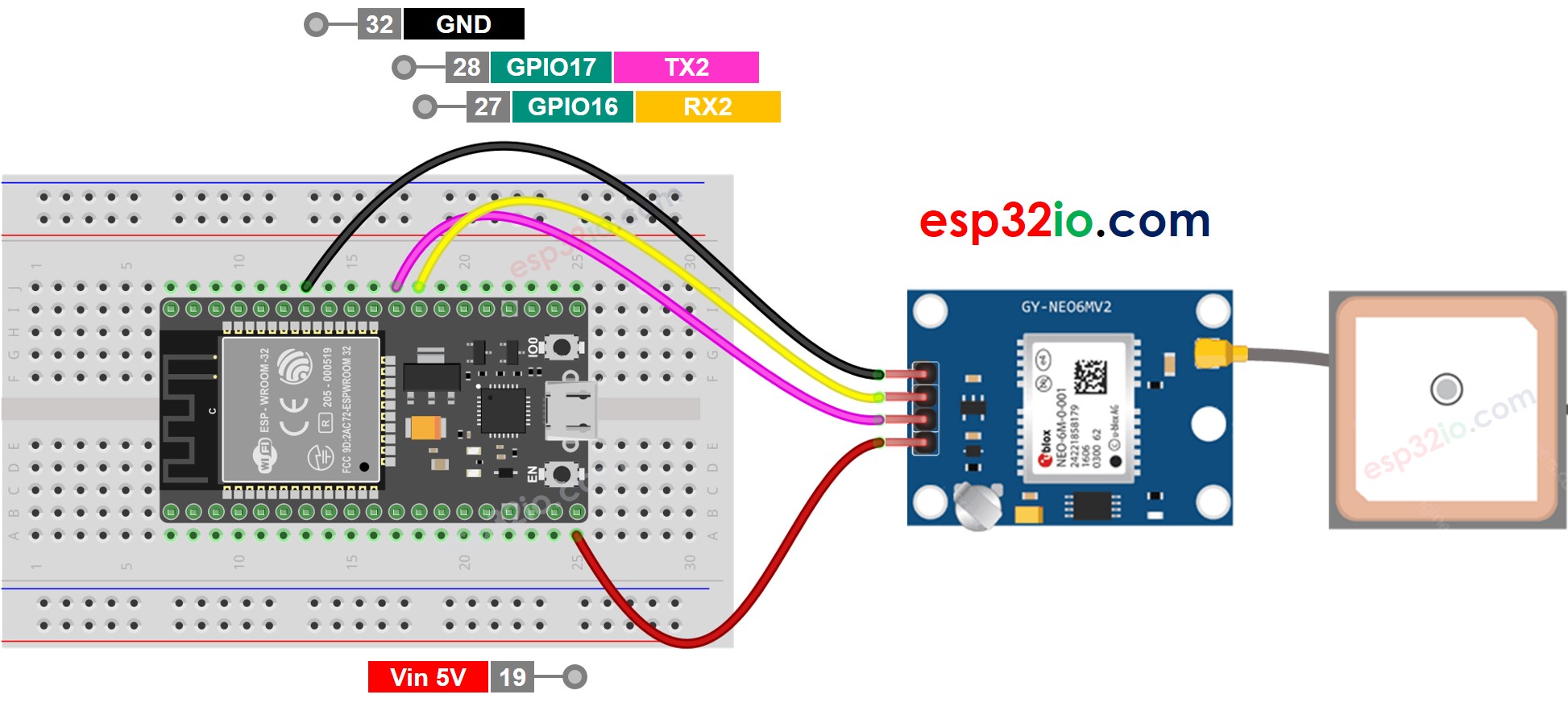
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
If you're unfamiliar with how to supply power to the ESP32 and other components, you can find guidance in the following tutorial: The best way to Power ESP32 and sensors/displays.
ESP32 Code
Reading GPS coordinates, speed (km/h), and date time
Quick Instructions
- If this is the first time you use ESP32, see how to setup environment for ESP32 on Arduino IDE.
- Do the wiring as above image.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your PC via a micro USB cable
- Open Arduino IDE on your PC.
- Select the right ESP32 board (e.g. ESP32 Dev Module) and COM port.
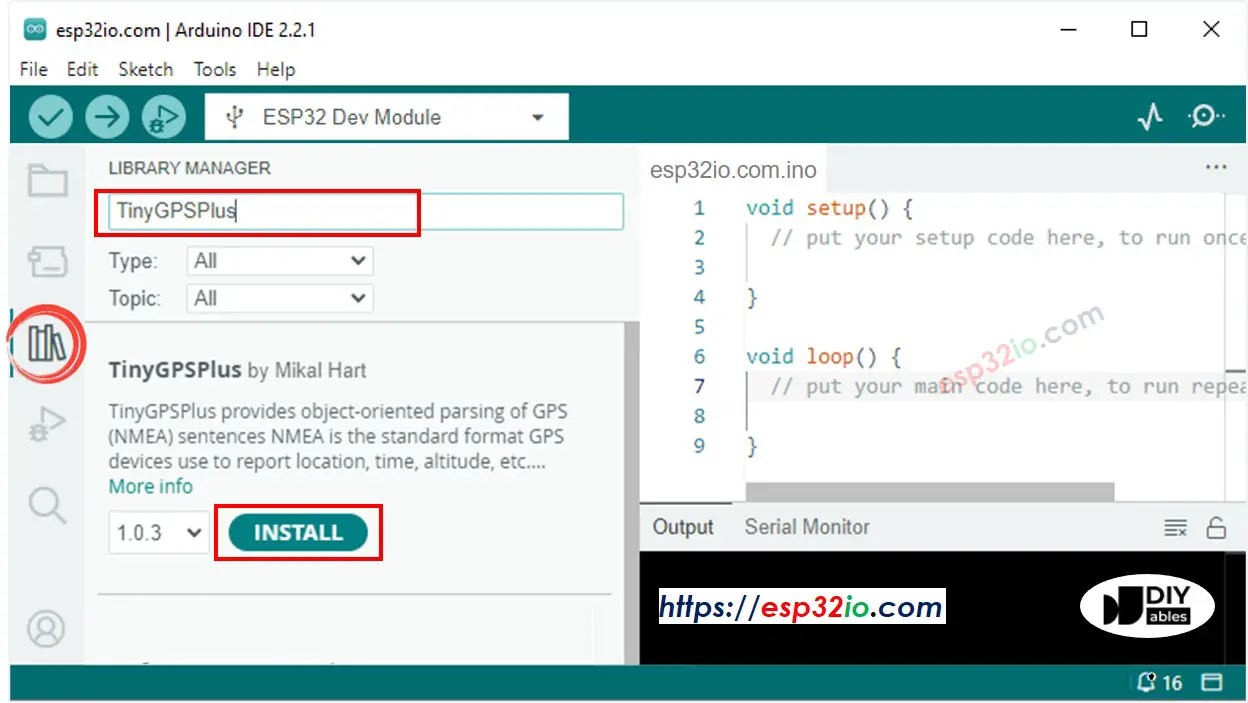
- On Arduino IDE, Go to Manage Libraries in the left bar
- Search “TinyGPSPlus”, then find the TinyGPSPlus library by Mikal Hart
- Click Install button to install TinyGPSPlus library.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP32
- See the result on Serial Monitor:
Calculating the distance from current location to a predefined location
The below code calculates the distance between the current location and London (lat:51.508131 , long: -0.128002)
Quick Instructions
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP32
- See the result on Serial Monitor:
Video Tutorial
Making video is a time-consuming work. If the video tutorial is necessary for your learning, please let us know by subscribing to our YouTube channel , If the demand for video is high, we will make the video tutorial.
