ESP32 - Potentiometer Triggers Relay
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP32 with the potentiometer to control relay. In detail:
- The ESP32 automatically turns relay on if the potentiometer's analog value is above a threshold
- The ESP32 automatically turns relay off if the potentiometer's analog value is under a threshold
We also learn how to convert the analog value to voltage and then use the voltage threshold to control relay:
- The ESP32 automatically turns relay on if the potentiometer's voltage is above a threshold.
- The ESP32 automatically turns relay off if the potentiometer's voltage is under a threshold.
We can extend this tutorial to use button to control a led strip, siren, light bulb, or motor... by connnecting them to the relay.
Hardware Used In This Tutorial
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Introduction to Relay and Potentiometer
We have specific tutorials about relay and potentiometer. Each tutorial contains detailed information and step-by-step instructions about hardware pinout, working principle, wiring connection to ESP32, ESP32 code... Learn more about them at the following links:
Wiring Diagram
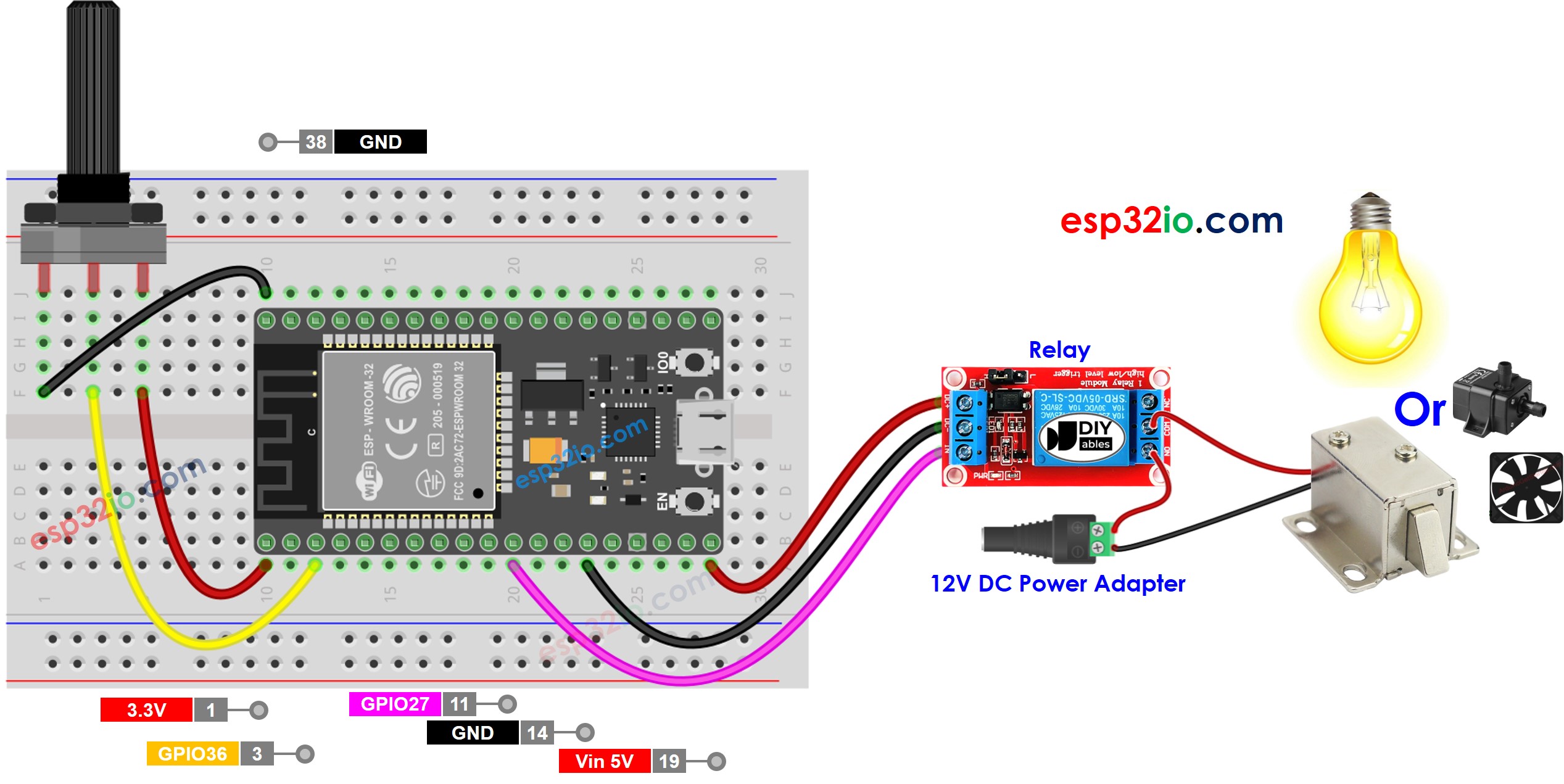
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
If you're unfamiliar with how to supply power to the ESP32 and other components, you can find guidance in the following tutorial: The best way to Power ESP32 and sensors/displays.
ESP32 Code - Analog Threshold
Quick Instructions
- If this is the first time you use ESP32, see how to setup environment for ESP32 on Arduino IDE.
- Do the wiring as above image.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your PC via a micro USB cable
- Open Arduino IDE on your PC.
- Select the right ESP32 board (e.g. ESP32 Dev Module) and COM port.
- Copy the above code and paste it to Arduino IDE.
- Compile and upload code to ESP32 board by clicking Upload button on Arduino IDE
- Rotate the potentiometer
- See the change of relay's state
Line-by-line Code Explanation
The above ESP32 code contains line-by-line explanation. Please read the comments in the code!
ESP32 Code - Voltage Threshold
The analog value read from the potentiometer is converted to voltage, and then the voltage is compared to a voltage threshold. If it exceeds the threshold, it triggers relay
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a potentiometer. The ESP32 ADC is good for projects that do NOT need high accuracy. However, for projects that need precise measurements, please note:
- The ESP32 ADC is not perfectly accurate and might need calibration for correct results. Each ESP32 board can be a bit different, so you need to calibrate the ADC for each individual board.
- Calibration can be difficult, especially for beginners, and might not always give the exact results you want.
For projects that need high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g ADS1115) with the ESP32 or using an Arduino, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still want to calibrate the ESP32 ADC, refer to ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver
Video Tutorial
Making video is a time-consuming work. If the video tutorial is necessary for your learning, please let us know by subscribing to our YouTube channel , If the demand for video is high, we will make the video tutorial.
