ESP32 - Potentiometer fade LED
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP32 with the potentiometer to change the brightness of LED.
If you want to trigger LED when the voltage of potentiometer reaches a threshold, see ESP32 - potentiometer triggers LED tutorial
Hardware Used In This Tutorial
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Buy Note: Want to make wiring easier? Try the LED Module. It already has a built-in resistor, so no extra parts needed!
Introduction to LED and Potentiometer
We have specific tutorials about LED and potentiometer. Each tutorial contains detailed information and step-by-step instructions about hardware pinout, working principle, wiring connection to ESP32, ESP32 code... Learn more about them at the following links:
Wiring Diagram
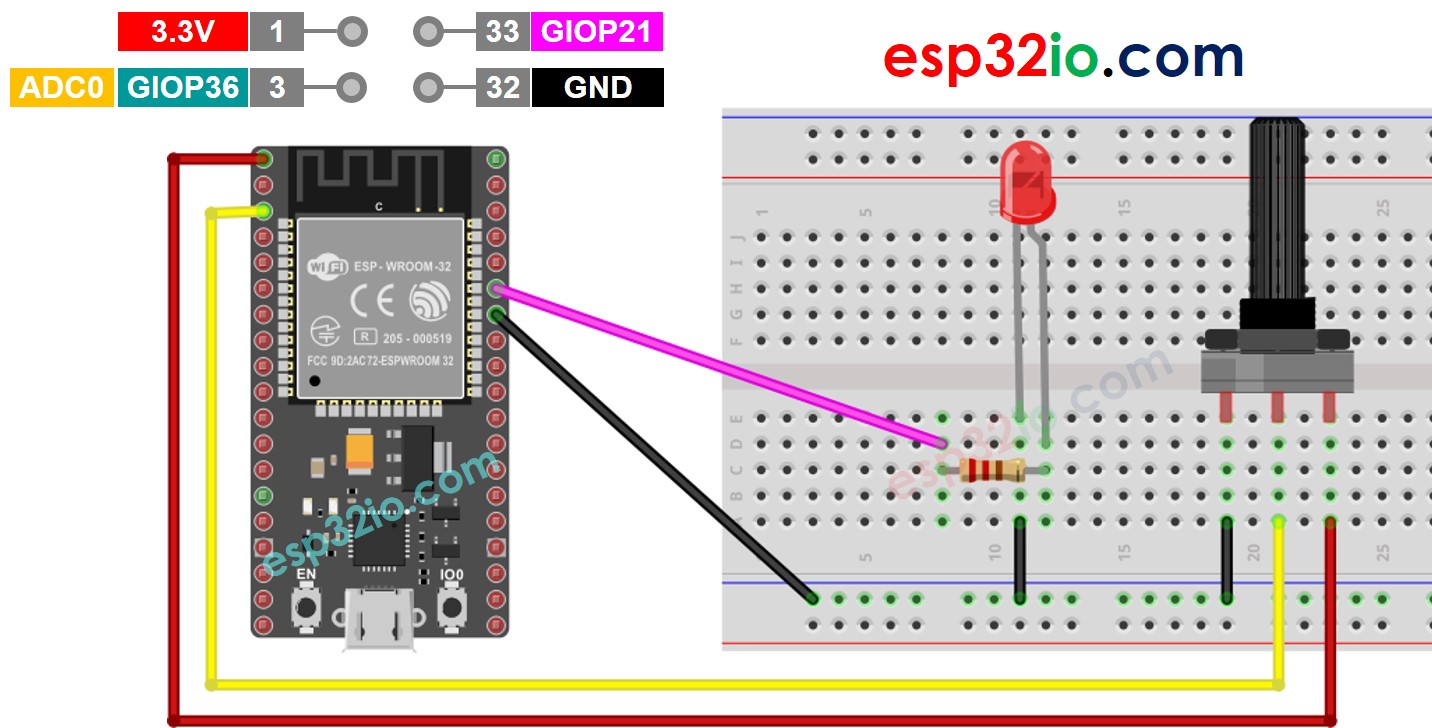
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
If you're unfamiliar with how to supply power to the ESP32 and other components, you can find guidance in the following tutorial: The best way to Power ESP32 and sensors/displays.
How To Program
- Reads the input on analog pin (value between 0 and 4095)
- Scales it to brightness (value between 0 and 255)
- Sets the brightness LED
ESP32 Code
Quick Instructions
- If this is the first time you use ESP32, see how to setup environment for ESP32 on Arduino IDE.
- Copy the above code and paste it to Arduino IDE.
- Compile and upload code to ESP32 board by clicking Upload button on Arduino IDE
- Open Serial Monitor on Arduino IDE
- Rotate the potentiometer
- See the LED fading
- See the result on Serial Monitor. It looks like the below:
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a potentiometer. The ESP32 ADC is good for projects that do NOT need high accuracy. However, for projects that need precise measurements, please note:
- The ESP32 ADC is not perfectly accurate and might need calibration for correct results. Each ESP32 board can be a bit different, so you need to calibrate the ADC for each individual board.
- Calibration can be difficult, especially for beginners, and might not always give the exact results you want.
For projects that need high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g ADS1115) with the ESP32 or using an Arduino, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still want to calibrate the ESP32 ADC, refer to ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver
Video Tutorial
Making video is a time-consuming work. If the video tutorial is necessary for your learning, please let us know by subscribing to our YouTube channel , If the demand for video is high, we will make the video tutorial.
